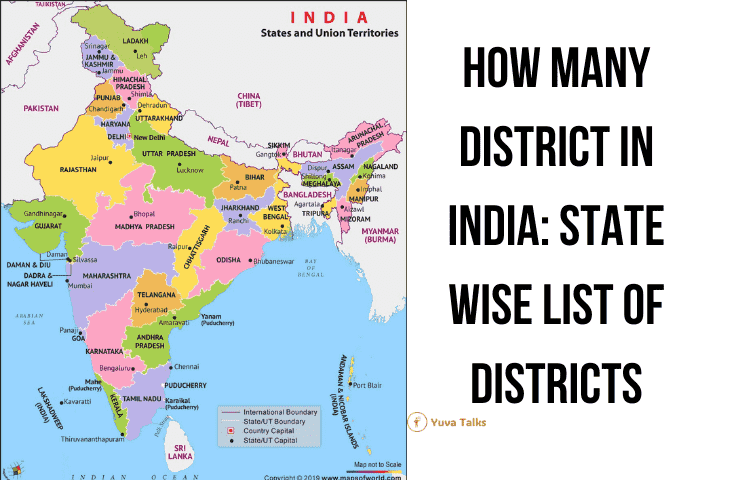
How Many Districts in India?
India consists of 806 districts according to the most recent data of 2024. Each district is a distinct administrative unit within the vast and populous country, contributing to India’s rich diversity in language, cuisine, and culture. The districts, which fall under the larger division of states, are overseen by magistrates and play a crucial role in governance. They ensure the implementation of policies and maintain law and order at the grassroots level. The uniqueness of each district is reflected in their varying sizes, populations, languages, cultural practices, and culinary traditions. Notably, the abbreviation for district is “Dist.”
What is a District?
A district is a territorial division in India that facilitates the efficient operation of administrative and judicial functions. As of 2024, there are a total of 80 districts in the country.
Also Read:- Which Is The Largest State In India In 2024
Administrative Functions of a District
The primary roles of districts include:
- Implementing national programs and policies at the local level.
- Acting as a liaison between state and central governments.
- Managing local disaster response and recovery efforts.
Comparative Analysis of Districts Worldwide
India is not alone in having districts, as countries like the US and China also have district-level governance structures.
In the US, these districts are known as counties, with a total of 3,006 counties across the nation. Similarly, China is divided into 1,355 counties. Sources to data: Census.gov
How Many States in India
The States Reorganisation Act of 1956 brought a transformative shift to India’s political landscape by creating states based on linguistic lines. This division resulted in the formation of 28 states and 8 Union Territories. Across the nation, there are 400 cities, including eight major metropolises: Bangalore, Hyderabad, Chennai, Pune, Ahmedabad, New Delhi, Mumbai, and Kolkata.
Each of India’s 28 states and 8 union territories boasts unique characteristics such as cuisine, language, and tourist attractions. Kerala is known for its tranquil backwaters, while Maharashtra is home to bustling cities. Rajasthan is famous for its grand forts, and Himachal Pradesh is celebrated for its picturesque valleys. These distinctive features contribute to India’s rich diversity and appeal. Each state and territory has its own leadership and plays a vital role in the country’s progress.
Also Read:- Top 10 Most Successful Women Entrepreneurs in India (2024)
How Many States in India with Their District Count, and Names
| STATES | DISTRICTS | NAME OF DISTRICTS |
| ANDHRA PRADESH | 13 | Allurisitharamaraju, Ananthapuramu, Annamayya, Anakapalli, Baptla, Chittoor, East Godavari, Eluru, Guntur, Kakinada, Konaseema, Krishna, Kurnool, Nandyal, N.T.R, Palnadu, Parvathipurammanyam, Prakasam, Srisathyasai, SPS Nellore, Srikakulam, Tirupati, Visakhapatnam, Vizianagaram, West Godavari, and YSR Kadapa |
| ARUNACHAL PRADESH | 26 | Anjaw, Changlang, Dibang Valley, East Kameng, East Siang, Itanagar, Kra Daadi, Kurung Kumey, Lohit, Longding, Lower Dibang Valley, Lower Subansiri, Namsai, Papumpare, Shiyomi, Siang, Tawang, Tirap, Upper Siang, Upper Subansiri, West Kameng, and West Siang. |
| ASSAM | 33 | Baksa, Barpeta, Bongaigaon, Cachar, Charaideo, Chirang, Darrang, Dhemaji, Dhubri, Dibrugarh, Dima Hasao, Goalpara, Golaghat, Hailakandi, Jorhat, Kamrup Metropolitan, Kamrup, Karbi Anglong, Karimganj, Kokrajhar, Lakhimpur, Majuli, Morigaon, Nagaon, Sivasagar, Sonitpur, South Salmara- Mankachar, Tinsukia, Udalguri, and West Karbi Anglong. |
| BIHAR | 38 | Araria, Arwal, Aurangabad, Banka, Begusarai, Bhagalpur, Bhojpur, Buxar, Darbhanga, East Champaran, Gaya, Gopalganj, Jamui, Jehanabad, Kaimur, Katihar, Khagaria, Kishanganj, Lakhisarai, Madhepura, Madhubani, Munger, Muzaffarpur, Nalanda, Nawada, Patna, Purnea, Rohtas, Saharsa, Samastipur, Saran, Sheikhpura, Sheohar, Sitamarhi, Siwan, Supaul, Vaishali, and West Champaran. |
| CHATTISGARH | 27 | Balod, Balodabazar Bhatapara, Balrampur, Bastar, Bemetara, Bijapur, Bilaspur, Dantewada, Dhamtari, Durg, Gariaband, Gaurela Pendra Marwahi, Jangir Champa, Jashpur, Kanker, Kawardha, Kondagaon, Korba, Korea, Mahasamund, Mungeli, Narayanpur, Raigarh, Raipur, Rajnandgaon, Sukma, Surajpur, and Surguja. |
| GOA | 2 | North Goa and South Goa |
| GUJARAT | 33 | Ahmedabad, Amreli, Anand, Arvalli, Banaskantha, Bharuch, Bhavnagar, Botad, Chhotaudepur, Dahod, Devbhumi Dwarka, Gandhinagar, Gir Somnath, Jamnagar, Junagadh, Kachchh, Kheda, Mahesana, Mahisagar, Morbi, Narmada, Navsari, Panchmahals, Patan, Porbandar, Rajkot, Sabarkantha, Surat, Surendranagar, Tapi, Dang, Vadodara, and Valsad. |
| HARYANA | 22 | Ambala, Bhiwani, Charkhi Dadri, Faridabad, Fathehabad, Gurugram, Hisar, Jhajjar, Jind, Kaithal, Karnal, Kurukshetra, Mahendragarh, Nuh, Palwal, Panchkula, Panipat, Rewari, Rohtak, Sirsa, Sonipat, and Yamunanagar. |
| HIMACHAL PRADESH | 12 | Bilaspur, Chamba, Hamirpur, Kangra, Kinnaur, Kullu, Lahaul and Spiti, Mandi, Shimla, Sirmapur, Solan, and Una. |
| JHARKHAND | 24 | Bokaro, Chaibasa, Chatra, Deoghar, Dhanbad, Dumka, Garhwa, Giridih, Godda, Gumla, Hazaribagh, Jamshedpur, Jamtara, Khunti, Koderma, Latehar, Lohardaga, Pakur, Palamu, Ramgarh, Ranchi, Sahibganj, Seraikela, and Simdega. |
| KARNATAKA | 30 | Bidar, Kalaburagi, Vijaypura, Yadagiri, Belagavi, Bagalkot, Raichur, Uttar Kannada, Dharwad, Gadag, Koppal, Ballari, Vijayanagar, Haveri, Davangere, Shivamogga, Udupi, Chikkamagaluru, Chitradurga, Dakshin Kannada, Kodagu, Hassan, Tumakuru, Mysuru, Mandya, Chamrajnagar, Ramanagara, Bengluru, Bengaluru Rural, Kolar, and Chikkaballapura. |
| KERALA | 14 | Alappuzha, Ernakulam, Idukki, Kannur, Kasaragod, Kollam, Kottayam, Kozhikode, Mallapuram, Palakkad, Pathanamthitta, Thrissur, Trivandrum, and Wayanad. |
| MADHYA PRADESH | 52 | Agar Malwa, Alirajpur, Anuppur, Ashokanagar, Balaghat, Barwani, Betul, Bhind, Bhopal, Burhanpur, Chhatarpur, Chhindwara, Damoh, Datia, Dewas, Dhar, Dindori, Guna, Gwalior, Harda, Indore, Jabalpur, Jhabua, Katni, Khandwa, Khargone, Mandla, Mandsaur, Mauganj, Morena, Narmadapurm, Narsinghpur, Neemuch, Niwari, Panna, Raisen, Rajgarh, Ratlam, Rewa, Sagar, Satna, Shehore, Seoni, Shahdol, Shajapur, Sheopur, Shivpuri, Sidhi, Singrouli, Tikamgarh, Ujjain, Umaria, and Vidisha. |
| MAHARASHTRA | 36 | Ahmednagar, Akola, Amravati, Aurangabad, Need, Bhandara, Buldhana, Chandrapur, Dhule, Gadchiroli, Gondia, Hingoli, Jalgaon, Jalna, Kolhapur, Latur, Mumbai City, Mumbai Suburban, Nagpur, Nanded, Nandurbar, Nashik, Osmanabad, Palghar, Parbhani, Pune, Raigad, Ratnagiri, Sangli, Satara, Sindudurg, Solapur, Thane, Wardha, Washim, and Yavatmal. |
| MANIPUR | 16 | Bishnupur, Chandel, Churachandpur, Pherzawl, Tengnoupal, Kakching, Noney, Imphal East and West, Jiribam, Kamjong, Kangpokpi, Senapati, Tamenglong, Thoubal, and Ukhrul. |
| MEGHALAYA | 11 | South West Garo Hills, West Garo Hills, North Garo Hills, East Garo Hills, South Garo Hills, West Khasi Hills, South West Khasi Hills, Easter West Khasi Hills, East Khasi Hills, Ri Bhoi, West Jaintia Hills, and East Jaintia Hills. |
| MIZORAM | 8 | Aizawl, Lunglei, Champhai, Mamit, Serchhip, Kolasib, Lawngtlai, Saiha, and Khawzawl. |
| NAGALAND | 11 | Dimapur, Kiphire, Kohima, Longleng, Mokokchung, Mon, Paren, Phek, Tuensang, Wokha, Zunheboto, Chumukedima, Niuland, Noklal, Shamator, and Tseminyu. |
| ORISSA | 30 | Angul, Balangir, Baleshwar, Bargarh, Bhadrak, Boudh, Cuttack, Deogarh, Dhenkanal, Gajapati, Ganjam, Jagatsinghpur, Jajpur, Jharsuguda, Kalahandi, Kandhamal, Kendrapara, Kendujhar, Khorda, Koraput, Malkangiri, Mayurbhanj, Nabarangpur, Nayagarh, Nuapada, Puri, Rayagada, Sambalpur, Subarnapur, and Sundargarh. |
| PUNJAB | 22 | Amritsar, Barnala, Bathinda, Faridkot, Fatehgarh Sahib, Fazilka, Ferozepur, Gurdaspur, Hoshiarpur, Jalandhar, Kapurthala, Ludhiana, Malerkotla, Mansa, Moga, Sas nagar, Sri Muktar Sahib, SBS Nagar, Pathankot, Patiala, Rupnagar, Sangrur, and Tarn Taran. |
| RAJASTHAN | 33 | Ajmer, Alwar, Banswara, Baran, Barmer, Bharatpur, Bhilwara, Bikaner, Bundi, Chittorgarh, Churu, Dausa, Dholpur, Dungarpur, Hanumangarh, Jaisalmer, Jaipur, Jalor, Jhalawar, Jhunjhunu, Jodhpur, Karauli, Kota, Nagaur, Pali, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Sawai Madhopur, Sikar, Sirohi, Sri Ganganagar, Tonk, Udaipur. |
| SIKKIM | 4 | Gangtok, Mangan, Gyalshinh, Namchi, Pakyong, and Soreng. |
| TAMIL NADU | 37 | Ariyalur, Chengalpattu, Chennai, Coimbatore, Cuddalore, Dharmapuri, Dindigul, Erode, Kallakurichi, Kancheepuram, Kanniyakumari, Karur, Krishnagiri, Madurai, Mayiladuthurai, Nagapattinam, Namakkal, Nilgiris, Perambalur, Pudukkottai, Ramanathapuram, Ranipet, Salem, Sivaganga, Tenkasi, Thanjavur, Theni, Thoothukudi, Tiruchirapalli, Tirunelveli, Tirupathur, Tiruvannamalai, Tiruvarur, Vellore, Viluppuram, and Virudhunagar. |
| TELANGANA | 33 | Adilabad, Hyderabad, Jagtial, Jangaon, Jayashankar Bhupalapally, Jogulamba Gadwal, Kamareddy, Karimnagar, Khammam, Bhadradri Kothagudem, Komaram Bheem Asifabad, Mahabubnagar, Mahabubabad, Mancherial, Medak, Medchal Malkajgiri, Mulugu, Nagarkurnool, Nalgonda, Narayanpet, Nirmal, Nizamabad, Pedapalli, Rajanna Sircilla, Rangareddy, Sangareddy, Siddipet, Suryapet, Vikarabad, Wanaparthy, Hanumakonda, Warangal, and Yadadri Bhuvanagari. |
| TRIPURA | 8 | Dhalai, Gomati, Khowai, North Tripura, Sepahijala, South Tripura, Unakoti, and West Tripura. |
| UTTAR PRADESH | 75 | Agra, Aligarh, Allahabad, Ahmednagar, Amroha, Auraiya, Azamgarh, Badaun, Bahraich, Ballia, Balrampur, Banda, Barabanki, Bareilly, and more. |
| UTTARAKHAND | 13 | Almora, Bageshwar, Chamoli, Champawat, Dehradun, Haridwar, Nainital, Pauri Garhwal, Pithoragarh, Rudraprayag, Tehri Garhwal, Udham Singh Nagar, and Uttarkashi. |
| WEST BENGAL | 23 | North 24 Parganas, South 24 Parganas, Bankura, Birbhum, CoochBihar, Dakshin Dinajpur, Darjeeling, Hooghly, Howrah, Jalpaiguri, jhargram, Kalimpong, Kolkata, Malda, Murshidabad, Nadia, Paschim Burdwan, Purba Burdwan, Paschim Medinipur, Purba Medinipur, Purulia, Uttar Dinajpur, and Alipurduar. |
Do you know how many districts are there in India? There are 766 total districts in India.
First District of India
Salem district holds a prominent place in India’s history, being the very first district established on April 4, 1792. For context, as of 2024, India is divided into a total of 806 districts. Initially, Salem district encompassed a vast area of 7,530 square kilometers, which included the present-day districts of Namakkal, Dharmapuri, and Krishnagiri. In its early years, Alexander Reed served as the district’s collector from 1792 to 1799, significantly shaping its initial administrative framework. This historical context underscores Salem’s importance as one of India’s earliest administrative units, contributing to the region’s rich historical heritage.
Also Read: Top 10 Most Expensive Paintings in the World 2024: Million-Dollar Artworks
Smallest District in India
The tiniest district in India is Mahe, covering an area of just 9 square kilometers. It has a total population of 41,934 residents.
Mahe, though small in area, draws tourists globally with its key attractions: Hillock and St. Theresa Shrine.
Despite its small population and size, the district encounters significant agricultural challenges.
The health of fishermen in the area has notably declined.
Largest District in India
The largest district in India isn’t solely defined by area; several factors contribute to its size:
- Population
- Geographical area
- Political significance
- Economic and historical aspects
Kachchh (Kutch) holds the title of the largest district in India. Let’s delve into its economy:
- Economic factors are crucial in defining the district’s size.
- Agriculture is the primary economic activity in the region.
- Recently, new industries have been established in Kachchh.
- The district is renowned for its trade activities.
- Kachchh is also a notable tourist destination.
The vast district of Kutch spans an area of 45,652 km² and has a population of approximately 2,092,371.
Most Populated and Least Populated Districts in India
Most Populated District:
The most populated district in India is North 24 Parganas, West Bengal, with a population of 10,082,852.
| State | District | Population |
| Maharashtra | Thane | 180.50 |
| West Bengal | North 24 Parangas | 160.9 |
| Karnataka | Bangalore | 126.7 |
| Delhi | Delhi East | 120.12 |
| Delhi | Delhi North | 118.34 |
| Maharashtra | Mumbai Suburban | 115.06 |
| West Bengal | Kolkata | 112.09 |
| Telangana | Hyderabad | 95.7 |
| Maharashtra | Pune | 94.27 |
| Gujarat | Ahmedabad | 87.79 |
Least Populated District:
The least populated district in India is Dibang Valley, Arunachal Pradesh, with a population of 8,004.
| State | District | Population |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Dibang Valley | 7,948 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Anjaw | 21,089 |
| Himachal Pradesh | Lahul and Spiti | 31,528 |
| Andaman & Nicobar | Nicobar | 36,842 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Upper Siang | 35,320 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Dibang Valley | 42,855 |
| Himachal Pradesh | Kinnaur | 84,298 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Kurung Kumey | 89,717 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Longding | 56,953 |
| Nagaland | Kiphire | 74,004 |
How Many Districts in Uttar Pradesh?
Uttar Pradesh, India’s largest state by area spanning 240,928 square kilometers, is divided into 75 districts. Established on January 24, 1950, each district is overseen by a District Magistrate from the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) for efficient governance. The state’s districts are organized into eighteen administrative divisions, each with its administrative headquarters. Uttar Pradesh, known for its large population, added three new districts in 2011 under Chief Minister Mayawati: Prabuddhanagar, Panchsheel Nagar, and Bhimnagar. With over 12 lakh residents, Uttar Pradesh remains one of India’s most populous states.
How Many Districts in India in 2024?
Kachchh stands out as a significant cultural and historical destination in India for several compelling reasons:
- It boasts a rich tapestry of diverse cultures, making it a melting pot of traditions and customs.
- The expansive Great Rann of Kachchh serves as a prominent geographical landmark, adding to the area’s allure.
- Kachchh is renowned for its ancient archaeological treasures, notably the site of Dholavira, offering insights into its historical significance.
- The region is celebrated for its exquisite native handicrafts and skilled leatherwork, adding to its cultural vibrancy and appeal.
India District Map: Uses and Functions
- Exploring Districts with Maps Utilize India’s district maps to discover towns, villages, rivers, tourist attractions, and cultural sites.
- Online Tools Leading resources like Google Maps, Maps of India, and Open Street Map provide comprehensive views of district layouts, aiding in detailed exploration.
Administration of Districts in India:
In India, district administration is managed by key officials who play crucial roles:
- District Magistrate, Deputy Commissioner, or District Collector: These officers, typically from the Indian Administrative Service (IAS), are responsible for administrative functions and revenue collection within the district.
- Superintendent of Police, Senior Superintendent of Police, or Deputy Commissioner of Police: Members of the Indian Police Service (IPS) who are tasked with maintaining law and order across the district.
- Deputy Conservator of Forests: An official from the Indian Forest Service (IFS) responsible for overseeing the district’s forests, environment, and wildlife conservation efforts.
These officials are supported by various state government officers. While most districts have a designated headquarters, some, such as Mumbai City in Maharashtra, Kolkata in West Bengal, Hyderabad in Telangana, and Chennai in Tamil Nadu, operate differently in terms of administrative structure.
Conclusion
In India, every district showcases distinct characteristics through its languages, culinary traditions, and fashion choices. For instance, regions like Bengal and Bihar predominantly see women adorning sarees, whereas in Punjab, traditional suits are preferred. Recognizing these diversities underscores the importance of fostering equitable growth and development across all districts.
The government has embarked on several initiatives to bolster district-level support. Programs such as Make in India and Digital India are pivotal in fostering economic opportunities and technological advancement throughout the nation. These efforts aim to empower every district, ensuring they play a vital role in India’s overall advancement and prosperity.
FAQs on How many districts in India?
Q1. What is a district?
Ans. A district is a regional administrative division within a state.
Q2. What is the largest district in India?
Ans Kachchh holds the title of India’s largest district, spanning across 45,674 square kilometers.
Q3. Who leads a district?
Ans Each district is overseen by a magistrate who acts as the executive responsible for regional development and policy implementation.
Q4. Which state has 38 districts?
Ans Uttar Pradesh, one of India’s largest states by population and area, is home to 38 districts.
Q5. Which district was India’s first?
Ans Salem district, established on April 4, 1792, was India’s inaugural district, encompassing what are now Namakkal, Dharmapuri, and Krishnagiri.
Q6. Which district is the smallest?
Ans Mahe in Puducherry claims the title of India’s smallest district, covering just 9 square kilometers.
Q7. Which state has the fewest districts?
Ans Among Indian states, Goa boasts the smallest number of districts with only 2.